INSTITUCION EDUCATIVA TECNICA INDUSTRIAL ESPAÑA
IETIE
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH
TENTH GRADE – Mr. OSCAR MENA
1. VOCABULARY ABOUT FAMILY
Exercise 1.Translate the vocabulary in
Spanish and practice the pronunciation.
a. Mother- mom → Mamá
b. Father – daddy – dad
c. Grandfather – grandpa
d. Grandmother
- grandma
e. Son
f. Daughter
g. Sister
h. Brother
i.
Aunt
j.
Uncle
k. Nephew
l.
Niece
m. Grandson
n. Granddaughter
o. Cousin
p. Stepmother
1. PRESENT CONTINUOUS
This verb form is used to talk about an action in
progress, could be at the moment to speak about it or in a longer term. The
present continuous (also named Present Progressive) may also be used to express
an event that is going to occur in the near future. Let’s see some examples:
Ø I am looking this beautiful landscape. (an action which is happening in this moment)
Ø I am looking this beautiful landscape. (an action which is happening in this moment)
Ø
Many
people are staying home to protect themselves from getting infected with COVID
19. (to describe a
temporary situation)
Ø
Nowadays,
the social nets are becoming the most useful tool for people to express their
opinions and feelings.
(to show an ongoing action in this time or a trend)
Ø
He
is arriving to Jamundi at 7:00 pm. (to express an action that is going to occur in the
near future)
Ø
¡Laura
is always reading! (to
emphasize in a repeated action)
3. PRESENT CONTINUOUS FORMS
3.1 Affirmative form
Examples:
Ø
My
father is working now.
Ø
I’m
studying English
Ø He’s fixing my bike.
Ø
We’re
playing soccer.
Ø
They’re
brushing their teeth.
Ø
It´s
flying high and fast.
3.1.1 ADDING -ing to the present participle verbs
A. Work – working, Paint – Painting, spell – spelling,
Watch – Watching
Go – going, do – doing, Sleep – sleeping, rain –
raining, speak – speaking.
B. Verbs which end in -e, quit it and add –
ing. Examples: dance – dancing, come – coming, take-
taking, write – writing, type – typing, arrive – arriving,
drive – driving, celebrate – celebrating, ride – riding.
C. Verbs that end in -y, just add -ing. Examples:
study – studying, play – playing, try – trying, fly – flying, buy –
buying, cry – crying, dry – drying, reply – replying.
D. Verbs ending in a single consonant preceded by a
vowel, double the consonant and add -ing. Examples: run – running, jog
- jogging, stop, stopping, sit – sitting, mop –
mopping (Exception: verbs ending in x, w and y).
3.2 Interrogative form Present Continuous
Ø Are you talking to me?
Ø Is my mom preparing the lunch?
Ø Is Aunt Emilia reading a magazine or a book?
Ø Are they playing soccer?
Ø Am I dreaming?
Ø Are you studying for the exam?
o 3.2.1Wh –
questions + Present Continuous
Examples.
Ø
What are you doing?
Ø
When is she coming to school?
Ø
Where is she studying English?
Ø
How’s your father doing?
Ø
Why are you working in this office?
3.3 Negative form Present Continuous
Examples:
Ø
I am not listening to her, I’m listening to
you.
Ø
She isn’t wearing a dress.
Ø
People aren’t obeying the lockdown rules.
Ø
Carlos isn’t paying attention to the teacher.
Ø
My girlfriend is not dancing, she’s sitting by me.
Ø
They aren’t sleeping, they are watching TV.
Exercise 3. Read the text and answer the questions
EXERCISE 4. See the picture and talk about what they
are doing.
Write a sentence about the people in the picture are
doing. Add -ing to the
main verb. Follow the example.
1. Carlos is _______________________________________.
2. My grandfather is ________________________________.
3. My aunt is ______________________________________.
4. My father is _____________________________________.
5. Carlos’ dad is ___________________________________.
6. My brother _____________________________________.
7. My mom´s _____________________________________.
8. My sister ______________________________________.
9. My cousin _____________________________________.
10. My cousin’s wife is _______________________________.
11. My neighbor is __________________________________.
12. Mrs. Ramirez is _________________________________.
13. My friend Felipe is _______________________________.
14. My teacher ____________________________________.
15. You __________________________________________.
16. We ___________________________________________.
17. My uncle’s _____________________________________.
18. My mother in-law is ______________________________.
19. My half- brother is ________________________________.
20. Arnulfo is _______________________________________.
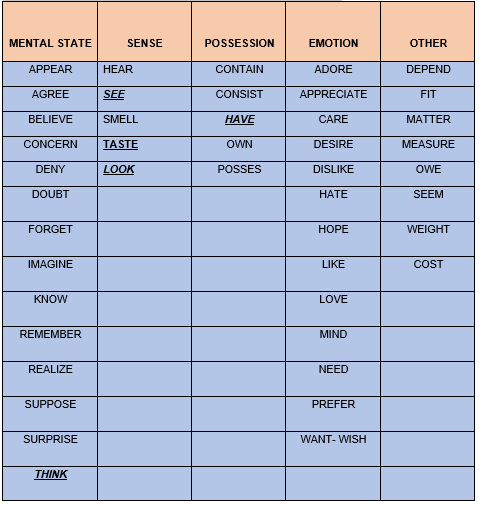
STATIVE VERBS
Some verbs are not used in present continuous. They
are named as stative verbs because they refer to states, relationships,
emotions and feelings rather than actions. They are used in Simple present. Let´s see them.
EXAMPLES:
Ø
I am
agreeing with the terms of the contract. X Incorrect
Ø
I
agree with the terms of the contract. ✓ Correct
Ø
She is
imagining with her wedding dress. X Incorrect
Ø
She
imagines wearing her wedding dress. ✓ Correct
Ø
We are
knowing the way we are walking. X Incorrect
Ø
We
know the way we are walking. ✓ Correct
Ø
She’s needing a book. X Incorrect
Ø
She needs a book. ✓ Correct
There are some exceptions to the
use of these stative verbs in
present continuous. For instance:
Verb
See
Ø
I see
Leidy not very clear, but I see her. (with the eyes)
Ø
I am
seeing Leidy. (date)
Verb
have
Ø
Sarah
has a beautiful cat. (she owns it)
Ø
She’s
having dinner. (she’s eating dinner)
Verb
look
Ø
My daughter
looks like me (resemble)
Ø
I’m
looking at you at this moment. (direct with eyes something)
Exercise
Choose
the present simple or present continuous (these verbs are sometimes stative)
1. She has (have) a bath every evening.
2. My husband _____________ (always / taste) the food
while I’m cooking! It’s very annoying.
3. A: Where’s Luke?
B: He is seeing(see) the doctor now.
4. I _____________ (not / think) that’s a good idea.
5. He
_____________ (have) a party at the weekend.
6. This coffee
_____________ (not / taste) right.
7. We _____________ (see) John and Susie next weekend.
8. What _____________ (you / think) about the war in
Iraq?
9. She _____________ (have) a headache.
10. It _____________ (be) cold today.
11. They _____________ (not / have) a car.
12. I _____________ (not / see) anything, I can’t work
the telescope.
13. The waiter _____________ (taste) the wine now.
14. She _____________ (not / be) a doctor.
15. A: What _____________ (that child / do)?
B: He _____________ (be) silly.
16. _____________ (you / be) hungry? _____________
(you / want) a sandwich?
17. A: What _____________ (you / do)?
B: I _____________ (think) about my ex-boyfriend.
18. I _____________ (have) fun today!
19. I _____________ (see) Julie every Tuesday.
20. I _____________ (have) an idea!
21. A: Achoo!
B: Bless you! _____________ (you / have) a cold?
22. They often _____________ (see) a film on Fridays.
23. A: How’s the cake?
B: It _____________ (taste) funny.
24. _____________ (you / have) a good time at the
moment?
25. The chef always _____________ (taste) the food
before he serves it.
26. A: Julie has been offered a new job.
B: Is she going to take it?
A: She _____________ (not / know). She _____________
(think) about it.